Pipeline Log
After your project has gone through the initial development and testing, knowing what is going on in runtime becomes important.
The Apache Hop Pipeline Log allows the logging of the activity of a pipeline with another pipeline. A Pipeline Log streams logging information from a running pipeline to another pipeline. The Pipeline Log will be created in JSON format.
Hop will pass the logging information for each pipeline you run to the pipeline(s) you specify as pipeline log metadata objects. In this post, we’ll look at an example of how to configure and use the pipeline log metadata to write pipeline logging information to a relational database.
The examples here are provided we use variables to separate code and configuration according to best practices in your Apache Hop projects.
Step 1: Create a Pipeline Log metadata object
To create a Pipeline Log click on the New → Pipeline Log option or click on the Metadata → Pipeline Log option.
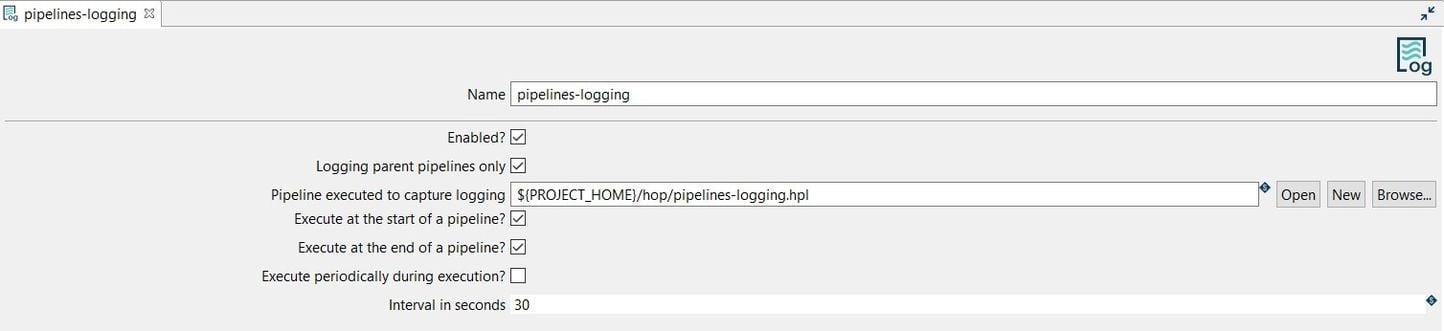
The system displays the New Pipeline Log view with the following fields to be configured.

The Pipeline Log can be configured as in the following example:
-
Name: the name of the metadata object (pipelines-logging).
-
Enabled: (checked).
-
Pipeline executed to capture logging: select or create the pipeline to process the logging information for this Pipeline Log
(${PROJECT_HOME}/hop/logging/pipelines-logging.hpl).
Next, select or create the pipeline to be used for logging the activity. We’ll create a pipeline soon, important to note is that you can use all the functionality in Apache Hop pipeline to work with the logging data. The only prerequisite is that the first transform in this pipeline needs to start with a pipeline logging transform.
-
Execute at the start of the pipeline?: (checked).
-
Execute at the end of the pipeline?: (checked).
-
Execute periodically during execution?: (unchecked)
Finally, save the Pipeline Log configuration.
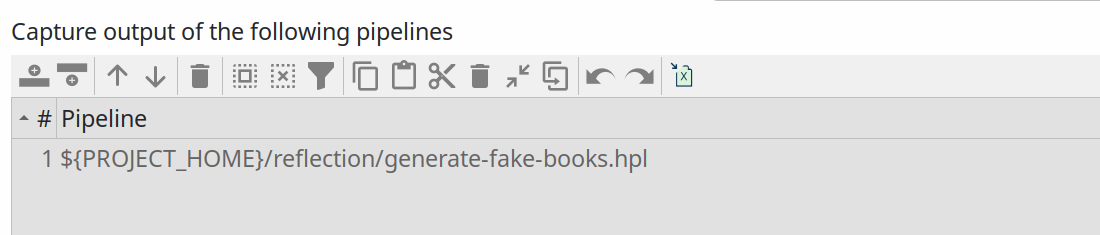
| pipeline logging will apply to any pipeline you run in the current project. That may not be necessary or even not desired. If you want to only work with logging information for a selected number of pipelines, you can add a selection of pipelines to the table below the configuration options ("Capture output of the following pipelines"). The screenshot below shows the single "generate-fake-books.hpl" pipeline that logging will be captured for in the default Apache Hop samples project. |
Step 2: Create a new pipeline with the Pipeline Logging transform
To create the pipeline you can go to the perspective area or by clicking on the New button in the New Pipeline Log dialog. Then, choose a folder and a name for the pipeline.
A new pipeline is automatically created with a Pipeline Logging transform connected to a Dummy transform (Save logging here).
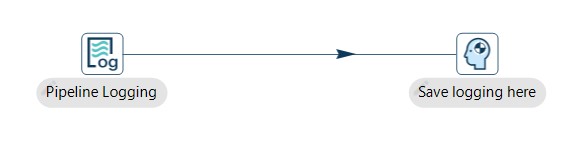
Now it’s time to configure the Pipeline Logging transform. This configuration is very simple, open the transform and set your values as in the following example:
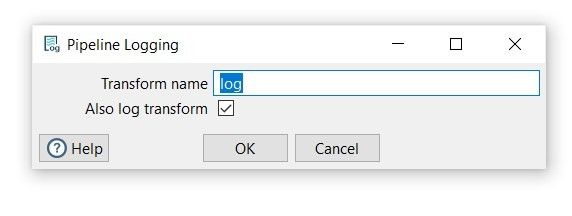
-
Transform name: choose a name for your transform, just remember that the name of the transform should be unique in your pipeline (log).
-
Also log transform: selected by default.
Step 3: Add and configure a Table output transform
The Table Output transform allows you to load data into a database table. Table Output is equivalent to the DML operator INSERT. This transform provides configuration options for the target table and a lot of housekeeping and/or performance-related options such as Commit Size and Use batch update for inserts.
| In this example, we are going to use a relational database connection to log but you can also use output files. In case you decide to use a database connection, check the installation and availability as a pre-requirement. |
Add a Table Output transform by clicking anywhere in the pipeline canvas, then Search 'table output' → Table Output.
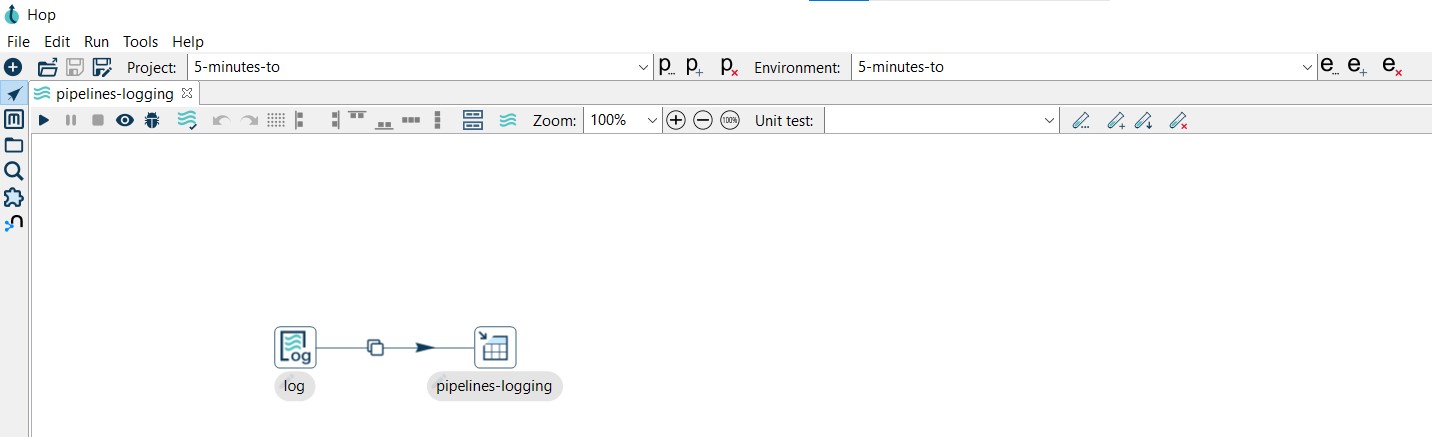
Now it’s time to configure the Table Output transform. Open the transform and set your values as in the following example:
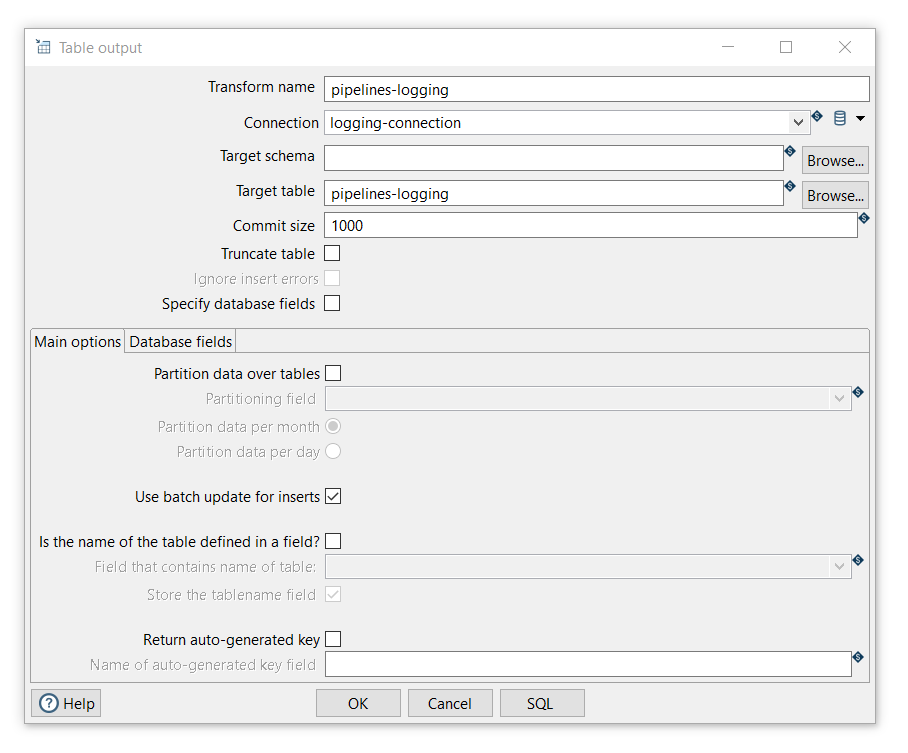
Transform name: choose a name for your transform, just remember that the name of the transform should be unique in your pipeline (pipelines logging).
-
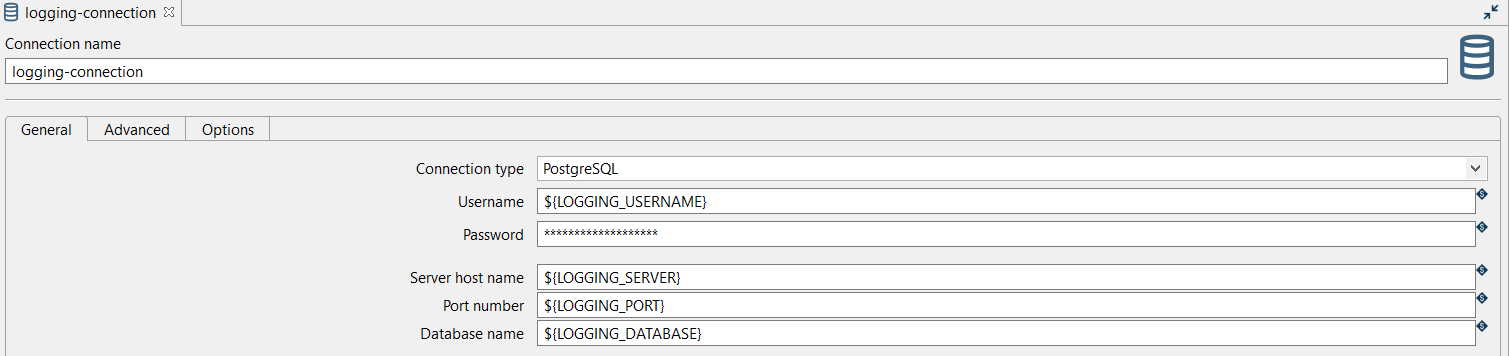
Connection: The database connection to which data will be written (logging-connection). The connection was configured by using the logging-connection.json environment file that contains the variables:
-
Target table: The name of the table to which data will be written (pipelines-logging).
-
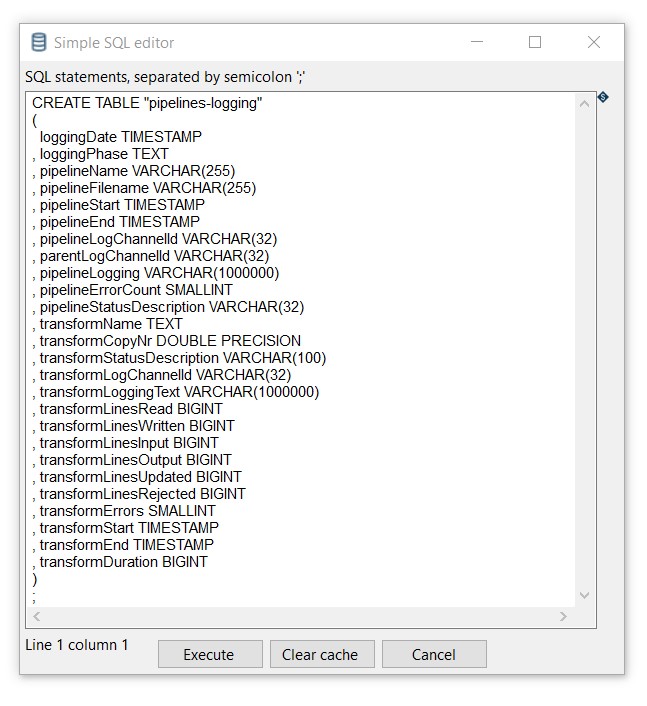
Click on the SQL option to generate the SQL to create the output table automatically:
-
Execute the SQL statements:
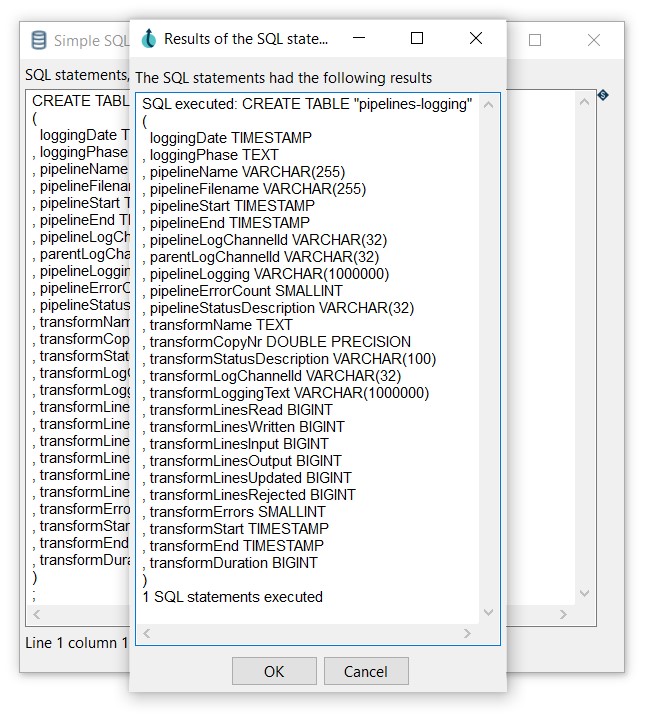
-
Open the created table in your favorite database explorer (e.g DBeaver) to see all the logging fields:
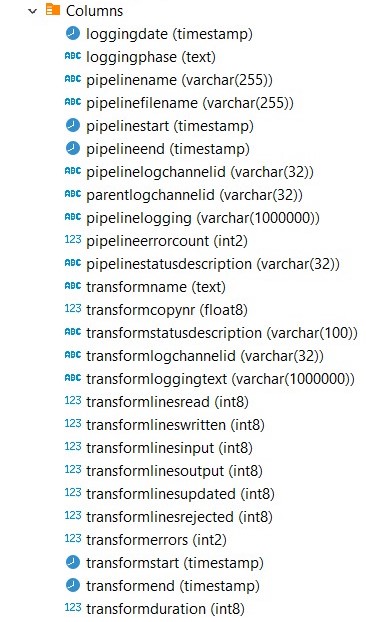
-
Close and save the pipeline.
Step 4: Run a pipeline and check the logs
Finally, run a pipeline by clicking on the Run → Launch option. In this case, we use a basic pipeline (generate-rows.hpl) that generates a constant and writes the 1000 rows to a CSV file:
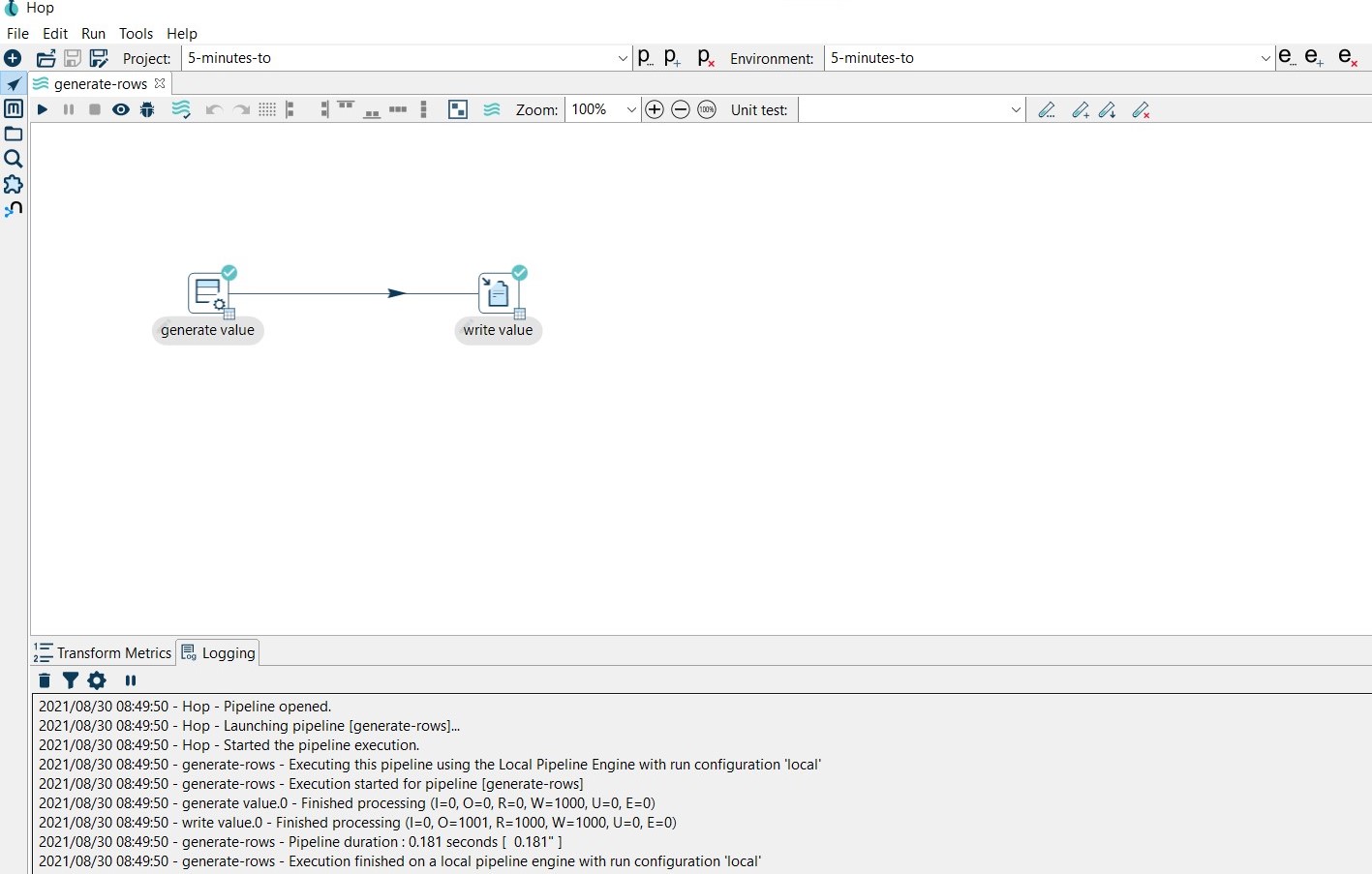
The data of the pipeline execution will be recorded in the pipelines-logging table.
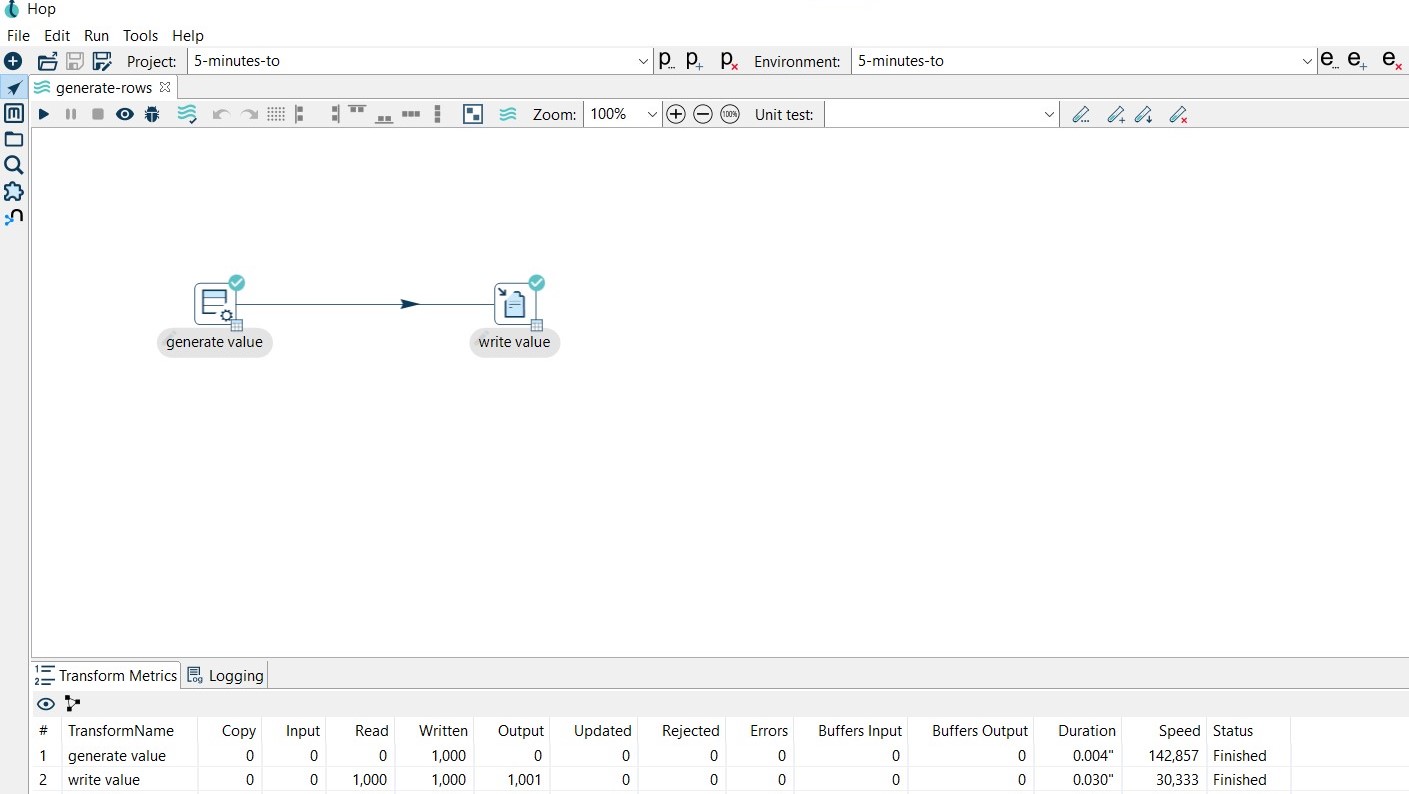
Check the data in the pipelines-logging table.

Next steps
You now know how to use the pipeline log metadata type to work with everything Apache Hop has to offer to process your pipeline logging information.
Check the related page on workflow log to learn how to set up a similar process to work with workflow logging.