Web Service
Introduction
Hop has a simple way of exposing data through a servlet.
For more information on configuring the Hop server check the Hop Server docs
Web Service Metadata
Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
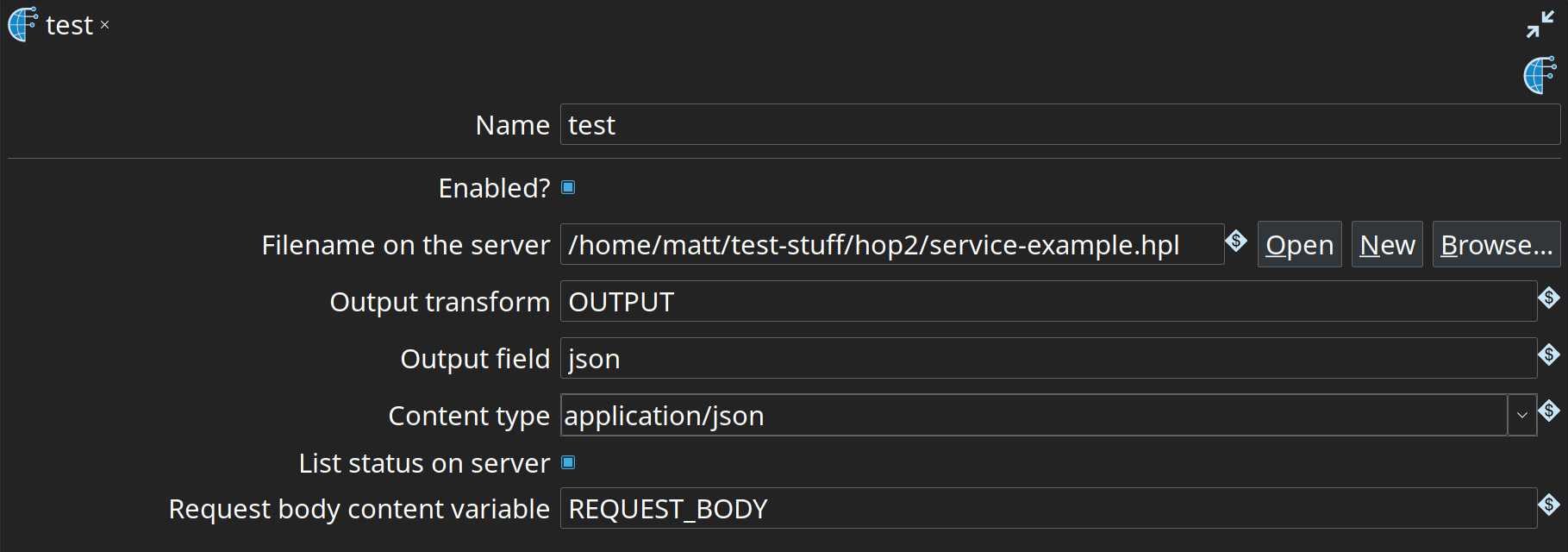
Name | The name of the web service. This is the name that is passed into the webService URL. |
Enabled | Enables or disabled the web service |
Filename on the server | This is the filename on the server. Make sure that the pipeline you want to execute is available on the server. |
Output transform | The name of the transform from which this service will take the output row(s). |
Output field | The output field from which this service will take data from, convert it to a String and output it |
Content type | The content type which will get reported by the webService servlet |
List status on server | Enable this option if you want the executions of the web service pipeline to be listed in the status of the server. |
Request body content variable | This is the name of the variable which at runtime will contain the content of the request body content. This is useful when doing a POST against the webservice. |
Hop Server configuration
Your Hop Server needs to know about the metadata you defined. As stated above you need to make sure the server has access to the pipeline(s) you want to execute as well as the server metadata.
The best way to do this is to set the following option in your XML configuration file:
<metadata_folder>/path/to/your/metadata</metadata_folder>A simple example would be:
<hop-server-config>
<hop-server>
<name>8181</name>
<hostname>localhost</hostname>
<port>8181</port>
</hop-server>
<metadata_folder>/home/hop/project/services/metadata</metadata_folder>
</hop-server-config>Using the service
Request parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| The name of the service. This corresponds to the Web Service metadata object. |
| The name of the pipeline run configuration. Please note that returning values is only supported on the "Local" pipeline engine. |
Any parameter name | Any parameter can be set simply by passing the value through the request URL |
Any variable name | Any variable can be set simply by passing the value through the request URL |
POST
Beside the default GET you can also do a POST against the web service and pass in a request body. The content of this body is then picked up if you set the request body content variable. This variable will contain the body content every time the POST request triggers the execution of the underlying pipeline.